It is appropriate for cleansing the teeth, prices very little, possesses varied medicative properties, and is definitely out there within the rural areas of the developing countries. it's conjointly an oral hygiene tool that needs no experience or special resources for its production.
Currently out there mouthrinses are available with a vigorous ingredient in an exceedingly mixture with organic solvents, viz., alcohol. A formulation of organic compound which will be hold on for an extended amount of your time and may be used with water has been according.
The inclusion of neem primarily based merchandise into future practice are a significant improvement over the prevailing practice.
I have previously posted about botanical description and anti-cancer properties of neem if you want to see that click the below link
https://plasubash.blogspot.com/2020/06/neem-tree-azadirachta-indica-elixir-in.html
NEEM AS ROOT CANAL IRRIGANT & ANTICANDIDASIS
Candida albicans and Enterococcus faecalis are the most predominant microorganisms recovered from root canals of teeth.
Thorough debridement of an inflamed root canal and whole removal of microorganisms are objectives of an powerful endodontic therapy.
Several in vitro studies have established that neem tree leaf extract could be a viable drug towards C. Albicans, E. Faecalis or maybe their blended state.
Sodium hypochlorite has been used as passage irrigant for decades; it reasons ability weakening of the tooth structure by lowering the hardness and structural integrity of the dentin inside the root canal.
To overcome this drawback herbal medication are used properly to inhibit E. Faecalis that reasons passage failure in patients undergoing endodontic treatment.
Its antioxidant and antimicrobial properties makes it a potential agent for root canal irrigation as an alternative to sodium hypochlorite.
Literature suggested that the Azadirachta indica leaf extract has nice antimicrobial impact towards E. Faecalis derived from infected root canal samples.
However, preclinical and medical trials are had to check biocompatibility and protection prior to Azadirachta indica will conclusively be advocated as an intracanal irrigating solution, however in vitro observation of Azadirachta indica effectiveness looks promising.
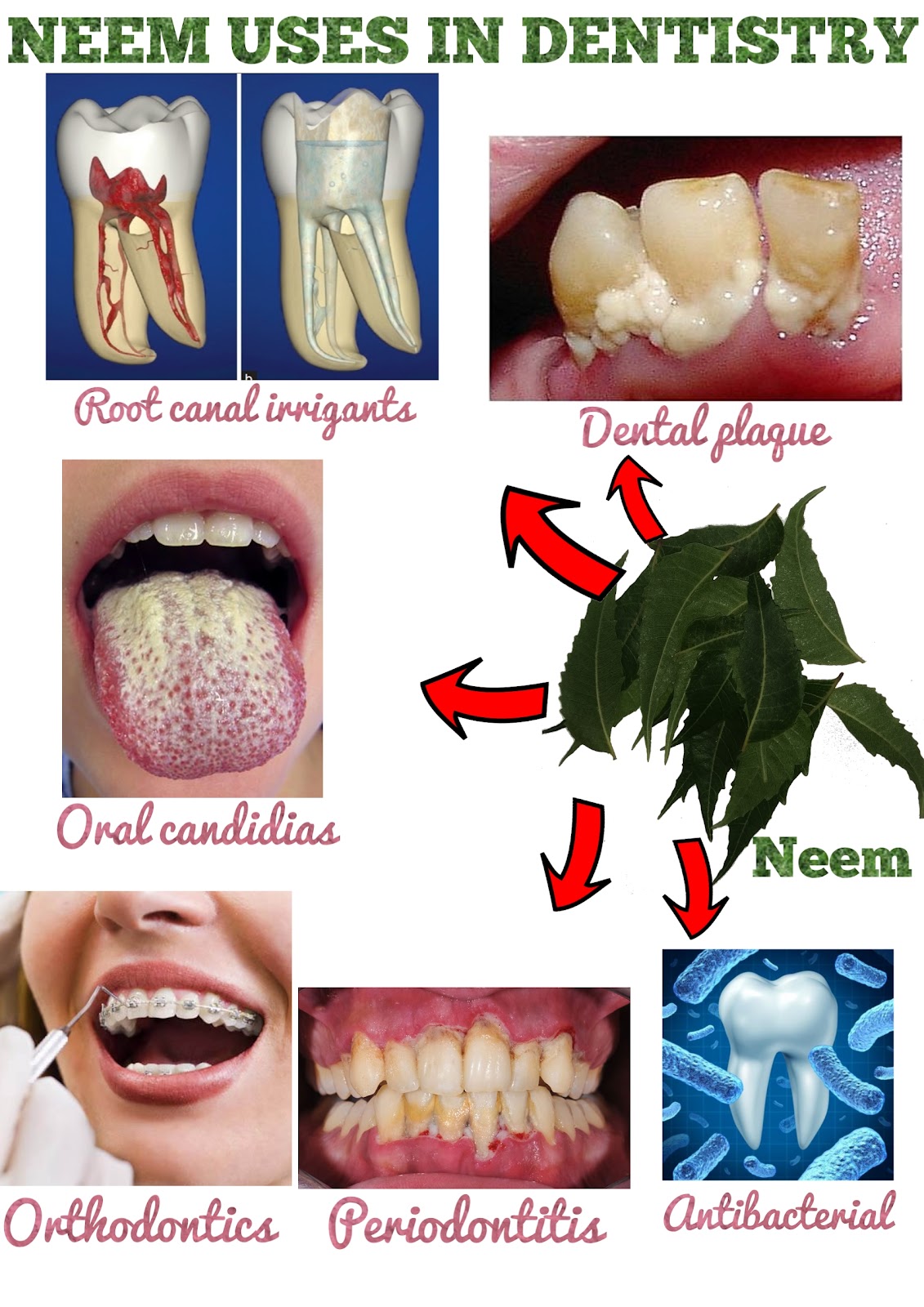
Root canal irrigants
Photo credit: www.saudiendodj.com
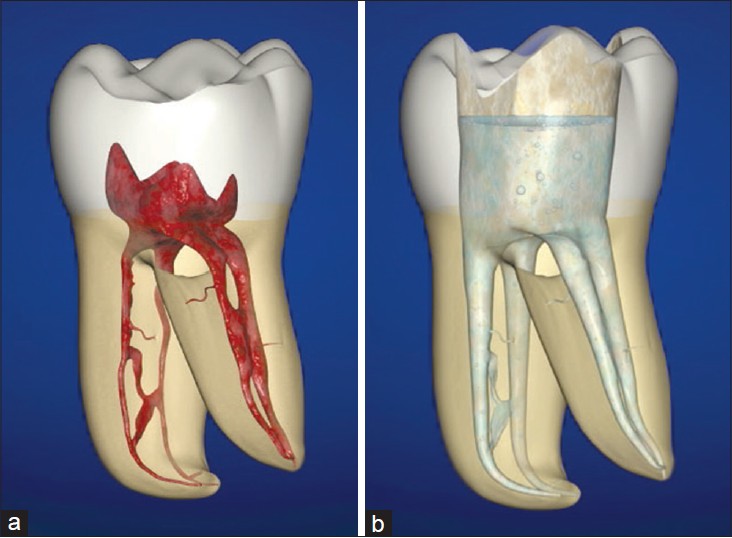
Oral thrush by Candida albicans
Photo credit:www.wikipedia.com
ANTI-PLAQUE ACTIVITY
Aqueous extract of Azadirachta indica stick and the gallotannin‑enriched extract from the Chinese sumac aphid suppressed insoluble glucan synthesis and ends up in microorganism aggregation.
It reduces the power of streptococci to colonize tooth surfaces.
Neem oil shows important bactericide activity and has been prompt to be used in treating dental plaque.
Mucoadhesive dental gel containing neem tree is found to be helpful in reducing the plaque index and salivary microorganism count relatively higher than chlorhexidine gluconate solution

Dental plaque
ANTICARIOGENIC ACTIVITY
Azadirachta indica extract showed antimicrobial activity against S. mutans, S. salivarius, S. sanguis and S. mitis. a combination of chew sticks is found to be useful in eradicating the dental caries‑causing organism.
Chloroform extract of neem tree leaf reserved strep mutans and strep salivarius and provides an aid for treating tooth decay.
The toothpaste containing Azadirachta indica as well as fluoridated toothpaste were equally efficacious against caries‑producing bacterium.
Acetone extract from the bark of Azadirachta indica is bactericidal against S. sobrinus thus indicates its anti‑cariogenic activity.
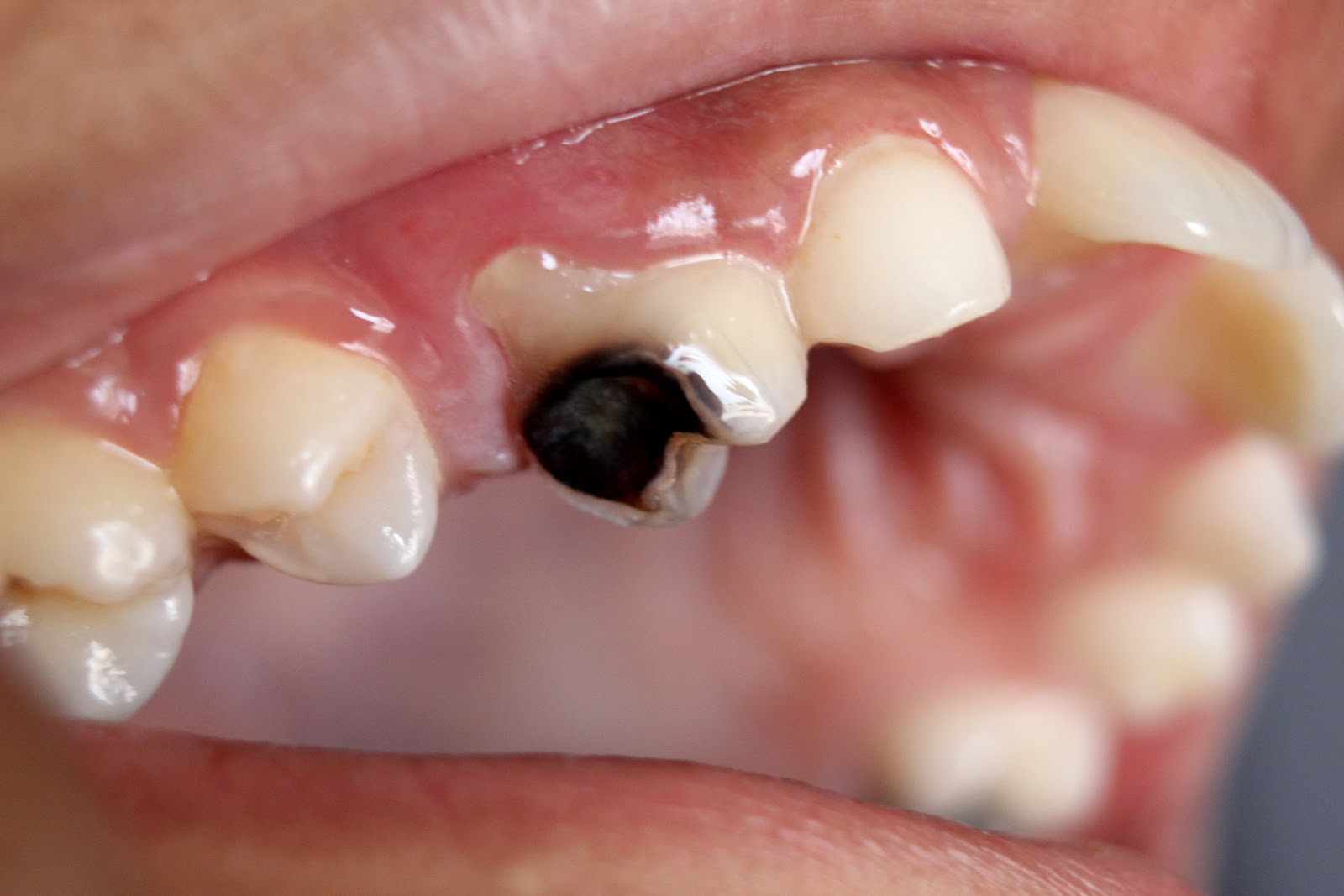
Dental caries
Photo credit: www.wikipedia.com
ANTIBACTERIAL EFFECT OF NEEM IN DENTAL CARIES
The microbial flora of the mouth is very complex, containing a large kind of microorganism species.
The most common oral disease, tooth decay is related to dental plaque and appear to occur once the conventional balance between the microorganisms and also the host is disturbed.
Extracts from Azadirachta indica sticks or bark are shown to inhibit the expansion of streptococcus mutans and important reductions in microorganism adhesion in vitro, suggesting that it will scale back the power of some streptococci to colonize tooth surfaces.
Neem extract made the maximum zone of inhibition on strep mutans at 50% concentration.
In addition, different strep species that are concerned within the development of dental caries appreciate strep salivarius, strep mitis and strep sanguis also are inhibited by Azadirachta indica extracts.
A considerable antibacterial activity of neem tree liquid extract on lactobacillus sp has conjointly been detected at higher concentrations.
ANTIBACTERIAL ACTIVITY
Antibacterial activity of the bark, leaf, seed, and fruit extracts of azadirachta indica (neem) on microorganism isolated from adult mouth and results disclosed that bark and leaf extracts showed bactericide activity against all the test bacteria used.
Furthermore, seed and fruit extracts showed bactericide activity solely at higher concentrations.
The antimicrobial effects of Azadirachta indica are reported against S. mutans and S. faecalis.
Ethanolic extract of neem tree leaves and sticks and bark exhibited significant antibacterial activity.
Dried chewing sticks of Neem showed most antibacterial activity against S. mutants compared to alternative dental caries‑causing organisms, S. salivarius, S. mitis, and S. sanguis.

Bacteria causing dental problems
Photo credit: www.idsli.com
EFFECT OF NEEM IN PERIODONTITIS
A study was created to assess the effectivity of Azadirachta indica supported mouth rinse concerning its antigingivitis effect and study confirmed that A. indica mouth rinse is equally effective in reducing periodontal indices as chlorhexidine
Brushing with Azadirachta indica dentifrice when each meal and using a mouthwash with Azadirachta indica extract is suggested treatment for preventing periodontitis.
In a study, Neem‑based mouth rinse was given to patients for assessing anti‑plaque and anti‑gingivitis activity.
The preparation of the water soluble azadirachtin is simple and may be instantly ready, It may be used as an adjunct to oral hygiene measures on a regular basis with none potential risks for tooth decay prevention moreover as periodontal issues.
Neem stick is found to be effective as a toothbrush in reducing dental plaque and gingival inflammation.
Studies indicate that leaf extract of A. indica‑based mouth rinse is highly efficacious which it should be used as another therapy within the treatment of periodontist
Azadirachta indica is very efficacious in the treatment of disease so exhibiting its biocompatibility with human periodontal fibroblast.

Periodontitis
Photo credit: www.msdmanuals.com
EFFECT OF NEEM IN ORTHODONTICS
- The primary acid‑tolerant microorganism related to dental plaque including
- streptococcus mutans
- streptococcus oralis
- streptococcus sobrinus
- Lactobacillus acidophilus
- streptococcus salivarius streptococcus mitis
- Streptococcus sangui
- streptococcus intermedius
- streptococcus anginosus
surround orthodontic appliances are a typical downside in several patients undergoing treatment. it's conjointly been reportable that presence of fixed orthodontic appliance greatly inhibits oral hygiene and creates new mindful areas for plaque and debris.
Ethanolic leaf extract of azadirachta indica shows important antibacterial activity against chosen acidogenic oral microorganism causing dental plaque in fixed orthodontic appliance patients.
The study conducted by us evaluated the anti‑plaque activity of the extract against S. mutans, S. sanguis, and S. mitis. The extract did not inhibit L. acidophilus once tested.
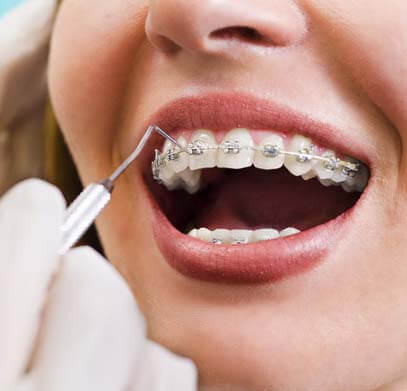
Orthodontic treatment
Photo credit:www.aestheticadentals
REFERENCE
- Prashant G M, Chandu G N, Murulikrishna K S, Shafiulla M D. The effect of mango and neem extract on four organisms causing dental caries: Streptococcus mutans, Streptococcus salivavius, Streptococcus mitis, and Streptococcus sanguis: An in vitro study. Indian J Dent Res 2007;18:148-51
- Kaushik A, Tanwar R, Kaushik M. Ethnomedicine: Applications of Neem (Azadirachta indica) in dentistry. Dent Hypotheses 2012;3:112-4
- Lakshmi T, Krishnan V, Rajendran R, Madhusudhanan N. Azadirachta indica: A herbal panacea in dentistry - An update. Phcog Rev 2015;9:41-4.
- Lakshmi T, Aravind Kumar S. Antibacterial evaluation of Azadirachta Indica ethanolic leaf extract against selected acidogenic oral bacteria causing dental plaque in fixed orthodontic appliance patients - An Invitro study. J Bot Res 2012;1:30‑40.
- Mohammad A. Alzohairy, Therapeutics Role of Azadirachta indica (Neem) and Their Active Constituents in Diseases Prevention and Treatment. Volume 2016, Article ID 7382506 https://doi.org/10.1155/2016/6
- Himanshu deswal, Yogender Singh, H.S.Grover, Amit Bhardwaj, Shalu Verma. Neem: A boon in medical and dental therapies: A review. Vol 4, Issue 2, 2016. ISSN - 2321-6832








0 Comments